Understanding the supplement manufacturing process is essential for anyone looking to enter the dietary supplement industry or evaluate the quality of their favorite products. This detailed process, from sourcing raw materials to producing a finished product, ensures that dietary supplements meet strict quality control measures and regulatory compliance. Key steps include developing a dietary supplement formula, testing raw materials for purity and potency, and using specialized equipment like a tablet press to create the final dosage form. Good manufacturing practices and FDA regulations help ensure that dietary supplements meet industry standards for quality and compliance.
1. Product Formulation: The First Step in Supplement Manufacturing
How Product Formulation Works
The formulation stage transforms a supplement idea into a marketable product. Experts design a dietary supplement formula by blending dietary ingredients to align with consumer health goals, such as promoting energy, supporting immune function, or aiding recovery.
This process involves collaboration between scientists, nutritionists, and product developers. They carefully balance ingredients to ensure safety, effectiveness, and compliance with dietary supplement industry standards.
Key Considerations in Supplement Formulation
Creating a well-formulated dietary supplement requires careful planning to ensure quality, safety, and effectiveness. The following are vital factors manufacturers must consider:
- Choosing the Right Ingredients: Ingredients are selected for their intended function, safety, and potential to deliver desired health benefits. Common ingredients include amino acids, well-absorbed mineral salts, herbal extracts, and organic acids.
- Dosage and Efficacy: Proper dosages are critical to ensure nutrient potency and meet product specifications.
- Regulatory Compliance: All formulations must comply with FDA regulations, ensuring ingredient safety and accurate dietary supplement labels.

2. Sourcing High-Quality Ingredients
Finding Reliable Ingredient Suppliers
The quality of any dietary supplement starts with sourcing high-grade raw material ingredients. Reliable suppliers provide raw materials that meet strict quality control standards, ensuring purity and consistency.
Manufacturers often seek non-GMO, organic, and sustainably sourced ingredients. This aligns with consumer preferences for clean-label products and positions brands competitively in the supplement industry.
Testing Raw Materials for Purity and Potency
Every batch of raw materials undergoes thorough testing for contaminants like heavy metals, pesticides, and harmful microbes. This step guarantees compliance with safety standards and ensures quality dietary supplements.
Many supplement manufacturers use third-party testing for additional assurance. Verified purity and potency can be highlighted on dietary supplement labels, fostering consumer trust in the finished product.

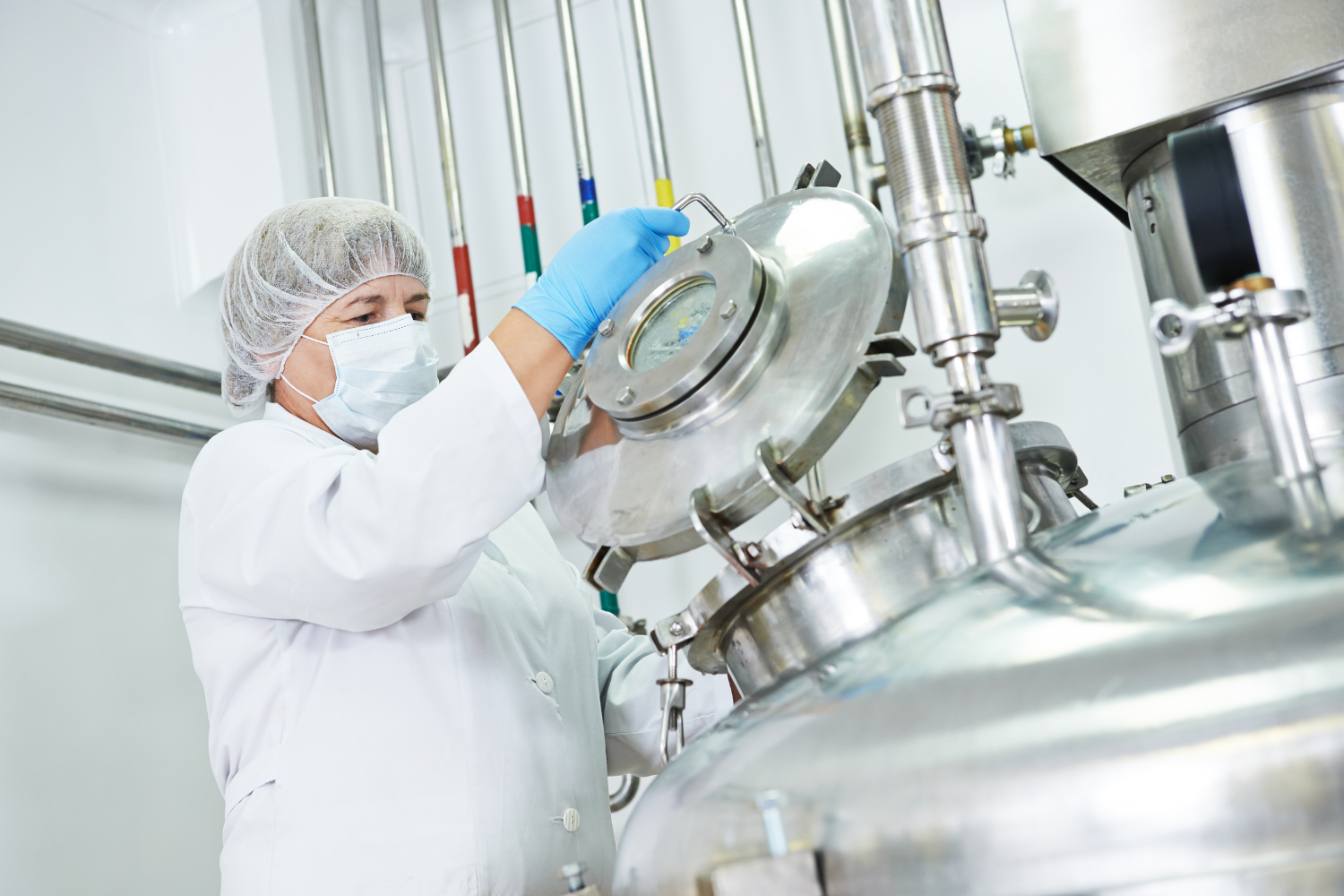
3. Supplement Manufacturing: The Production Process
The supplement manufacturing process involves several key steps to turn raw materials into finished products ready for consumers. Each stage is designed to maintain quality, consistency, and compliance with industry standards.
1. Blending the Ingredients
Once raw materials arrive and are verified through testing for contaminants, potency, and nutrient content, they are carefully blended into a uniform mixture. This step ensures that each dose contains the exact proportions of active dietary ingredients, such as amino acids, well-absorbed mineral salts, and herbal extracts, required for the dietary supplement formula.
Blending requires specialized equipment, such as ribbon mixers for powders or high-shear blenders for liquids. Dry blending is typically used for protein powders and organic acids, while liquid blending is essential for liquid supplements. The goal is consistent nutrient potency across the entire production batch, ensuring the product maintains its intended health benefits.
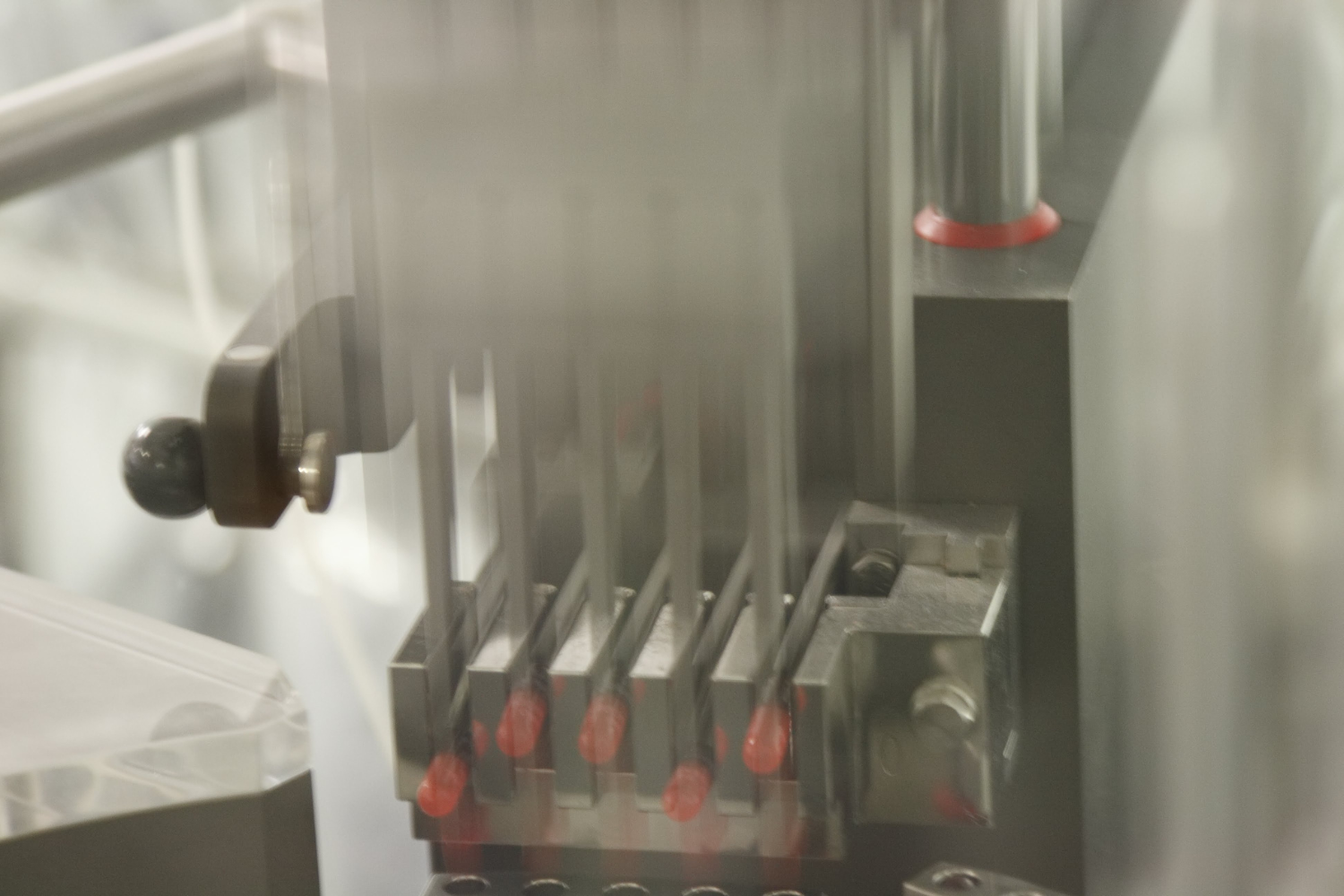
2. Encapsulation, Tableting, or Powder Filling
After blending, the supplement moves to its final dosage form, a critical step in the manufacturing dietary supplements process.
Types of Supplements Produced:
- Capsules: Blended ingredients are precisely measured and encapsulated into gelatin or plant-based capsules. This dosage form is favored for its easy swallowing and accurate nutrient delivery.
- Tablets: Ingredients are compressed into solid tablets using a tablet press. Tablets may include coatings to improve usability and shelf life.
- Powders: The mixture is portioned into tubs, sachets, or pouches for consumers to mix with liquids. This form is prevalent for fitness-focused supplements due to its flexibility in dosage.
Capsules and tablets offer convenience, while powders allow for flexible dosing options. Selecting the proper form depends on the target market and the supplement’s intended use.

3. Coating (For Tablets)
Tablets often receive a specialized coating to enhance usability and protect their integrity. Coatings make tablets easier to swallow and shield them from moisture, oxidation, or light, which can degrade the active ingredients.
Coatings mask unpleasant tastes or odors associated with raw material ingredients, ensuring a more consumer-friendly experience. Advanced coating techniques provide durability, protecting tablets to maintain quality during storage and transportation.
4. Quality Control During Manufacturing
Quality control is critical at every stage of manufacturing dietary supplements. Samples are collected and tested during blending, encapsulation, and packaging to ensure the finished product meets dosage accuracy, consistency, and appearance specifications.
State-of-the-art laboratory equipment, including high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) and in-house microbiological labs, helps manufacturers monitor product integrity. These quality control measures ensure that finished products comply with regulatory requirements, like FDA regulations, and maintain high standards for consumer safety.
4. Testing and Quality Assurance
Before supplements reach the market, they undergo comprehensive testing to verify safety, potency, and compliance with industry regulations. These tests are essential to building consumer trust and ensuring product reliability.
Tests Include:
- Microbial Testing: Verifies products are free from harmful bacteria, yeast, and mold that could compromise microbiological compliance.
- Heavy Metals Testing: Ensures compliance with heavy metal limits by screening for contaminants such as lead, arsenic, and mercury.
- Potency Testing: Confirms that the labeled amounts of critical ingredients match the product’s content, ensuring consistent nutrient potency.
Third-Party Testing for Transparency
Many supplement manufacturers opt for third-party testing to provide an extra layer of quality assurance. Independent labs verify that supplements meet stringent quality and safety standards, offering unbiased evaluations. Certifications from organizations like NSF International, USP (United States Pharmacopeia), or Informed-Choice can be displayed on dietary supplement labels, reinforcing consumer confidence.
Third-party testing verifies quality and safety, helping brands meet consumer expectations and build trust.

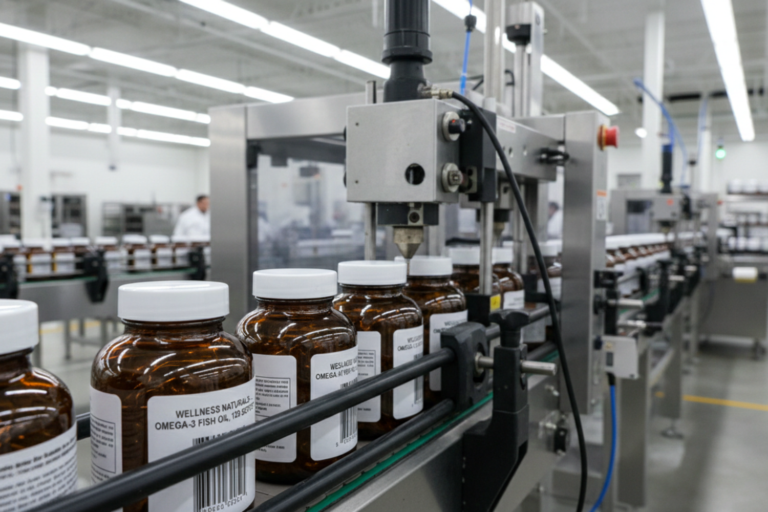
5. Packaging and Labeling
Packaging and labeling are crucial steps in the supplement manufacturing process. Proper packaging safeguards dietary supplements from environmental factors like light, heat, and moisture, which can compromise quality. Meanwhile, accurate labeling ensures regulatory compliance and helps build consumer trust. Manufacturers select packaging options based on the type of supplement and target audience preferences.
Popular Packaging Options:
- Bottles: Common for capsules, tablets, and soft gels, bottles are typically sealed to maintain freshness and safety.
- Jars and Tubs: Ideal for powders, such as protein powders or pre-workout supplements, offering durability and ease of use.
- Blister Packs: These are used for individual capsules or tablets, providing convenient and secure storage and protecting the product from contamination.
- Sachets or Stick Packs: Single-serving packets for powders or liquids, perfect for on-the-go use and accurate dosing.
Labeling for Compliance and Marketing
Labels are vital to dietary supplement manufacturing, serving both compliance and marketing purposes. FDA guidelines require manufacturers to provide accurate information about the product, including its contents, serving size, and usage instructions. Incorrect or misleading labels can result in regulatory actions.
Key Labeling Elements:
- Ingredient List: Lists active and inactive ingredients, specifying the amount of each.
- Supplement Facts Panel: Displays serving sizes, servings per container, and the daily value percentage of each nutrient.
- Health Claims: Claims about health benefits must be supported by scientific evidence, and it cannot be stated that the product prevents, treats, or cures diseases.
- Other Required Information: Includes manufacturer details, expiration dates, and information about potential allergens.

Branding and Marketing Considerations
Packaging and labeling should resonate with your target audience. Eco-friendly packaging appeals to consumers focused on sustainability, while bold, modern designs often attract fitness enthusiasts. High-quality packaging also reinforces the perception of a premium product.
Including third-party certifications such as “Non-GMO,” “Organic,” or “Vegan” on the label can enhance credibility. These certifications align with consumer preferences and can increase confidence in your product’s quality and safety.
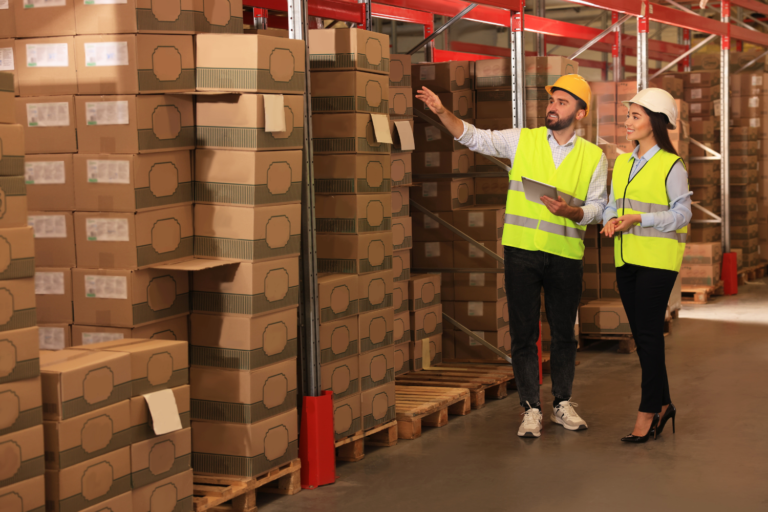
6. Distribution and Shipping
Once supplements are manufactured and packaged, the next step is distribution. Companies may sell through their own e-commerce platforms, online marketplaces like Amazon, or retail partnerships with health food stores or pharmacies. Selecting the right channels helps maximize reach and sales.
Efficient logistics management is critical for maintaining inventory levels, timely shipping, and customer satisfaction. Many businesses partner with fulfillment services or use solutions like Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) to handle storage, packing, and delivery seamlessly.
International Distribution
Expanding into international markets requires adherence to each country’s specific regulations. For example, some nations impose restrictions on certain dietary ingredients or require unique dietary supplement labels. Ensuring compliance with local laws is key to successful global distribution.
Researching import regulations, certification requirements, and tariff codes for target markets is essential. Planning for international shipping logistics and understanding duties and taxes ensures smooth operations and opens your business to new growth opportunities.

7. Compliance and Regulatory Considerations
In the U.S., the FDA regulates dietary supplements to ensure consumer safety and product quality. Manufacturers must comply with the Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act (DSHEA) and operate in facilities that adhere to Current Good Manufacturing Practices (cGMP). These regulations help ensure that supplements meet safety, quality, and labeling requirements before reaching the market.
Key Compliance Areas:
- cGMP Compliance: Manufacturing facilities must follow cGMP guidelines to ensure proper design, monitoring, and production control. These standards reduce risks related to contamination, formulation errors, or incorrect labeling.
- Adverse Event Reporting: Manufacturers must document any adverse events reported by consumers. Serious cases must be reported to the FDA to maintain transparency and accountability.
Avoiding Misleading Claims
Avoiding unverified or misleading health claims is essential to regulatory compliance. Products cannot claim to “cure,” “treat,” or “prevent” diseases unless supported by FDA approval, which supplements do not typically receive. Instead, manufacturers should focus on structure/function claims, such as “supports immune health” or “promotes joint mobility,” which describe the role of the supplement in maintaining normal body function.
Mastering the Supplement Manufacturing Process
The supplement manufacturing process is a detailed operation involving formulation, ingredient sourcing, blending, quality control, packaging, and compliance with regulations. Each step is critical in delivering high-quality, safe, and effective dietary supplements.
Understanding these stages enables businesses to meet consumer expectations while adhering to industry standards. Mastering this process is crucial in launching or expanding a successful supplement brand that builds trust and consistent repeat sales.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does the supplement manufacturing process take?
The process typically takes several weeks to months, depending on the complexity of the formulation, testing requirements, and packaging specifications. Custom formulations often require more time than stock options.
Do supplements require FDA approval before they can be sold?
No, the FDA does not approve dietary supplements before they are sold. However, manufacturers must follow FDA regulations, including proper labeling, adherence to cGMP standards, and ensuring safety.
What is cGMP, and why is it important?
cGMP (Current Good Manufacturing Practices) is a set of FDA regulations that ensure supplements are consistently manufactured to meet safety and quality standards. Compliance with cGMP is critical for producing reliable, effective products.
How do I choose the right manufacturer for my supplements?
Choose a manufacturer with cGMP certification, a strong industry reputation, and expertise in your desired supplement type. Look for third-party certifications and the capability to offer custom formulations to meet specific business needs.
What types of testing are involved in supplement manufacturing?
Testing includes verifying purity, potency, and the absence of contaminants like heavy metals and microbes. Final product testing ensures the supplement contains the correct dosages and meets all label claims, providing quality assurance for consumers.
References
- National Institutes of Health, Office of Dietary Supplements (n.d.). Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994. https://ods.od.nih.gov/About/DSHEA_Wording.aspx
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024). Dietary Supplements – FDA. https://www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2022). FDA 101: Dietary Supplements. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/fda-101-dietary-supplements
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2005). Dietary Supplement Labeling Guide: Chapter I. https://www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/dietary-supplement-labeling-guide-chapter-i-general-dietary-supplement-labeling
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024). Guidance Documents & Regulatory Information by Topic (Food and Dietary Supplements). https://www.fda.gov/food/guidance-regulation-food-and-dietary-supplements/guidance-documents-regulatory-information-topic-food-and-dietary-supplements
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2024). Questions and Answers on Dietary Supplements. https://www.fda.gov/food/information-consumers-using-dietary-supplements/questions-and-answers-dietary-supplements