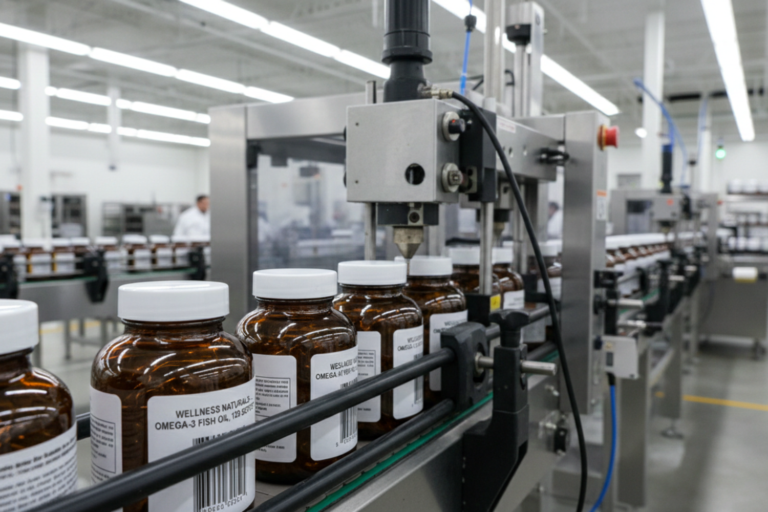
A single mistake in supplement packaging and logistics can result in damaged inventory or product recalls. A cracked seal, a shipment left in high heat, or a missing label may seem minor, but each can disrupt fulfillment and harm brand credibility. Packaging choices and logistics planning influence how well dietary supplements withstand storage, transportation, and delivery.
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) enforces 21 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 111, which outlines the manufacturing, packaging, labeling, and holding standards for dietary supplements. These rules are designed to ensure consistency and prevent contamination during processing. When those standards are not met, products risk non-compliance, spoilage, or labeling errors that can lead to costly recalls.
Many supplement brands work with professional supplement fulfillment services or nutraceutical logistics providers that maintain climate-controlled facilities and follow Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP)-aligned practices for holding and distribution under 21 CFR 111.453 and 111.470. These standards guide how supplements are stored and transported to maintain product quality, including the use of temperature monitoring, insulated containers, and documented handling procedures. Their role is to help brands keep products compliant, safely packaged, and ready for sale. Effective supplement packaging and logistics are essential to consistent quality control and lasting customer trust.
What Are the Key Packaging Requirements for Supplements
Proper packaging safeguards supplement products from damage, moisture, and mislabeling. The right packaging materials also ensure compliance with FDA regulations and reduce the risk of contamination during distribution.
How to Choose the Right Materials and Labeling
Each packaging format performs differently under transport and storage conditions, and the right choice depends on the product’s physical form and environmental sensitivity.
- Select packaging by format and sensitivity. Bottles, jars, pouches, and blister packs suit different products. For example, probiotic capsules often require moisture-resistant bottles with desiccants to maintain stability, while protein powders and drink mixes are better preserved in foil-lined pouches that limit exposure to humidity.
- Reduce exposure to damaging elements. Effective packaging solutions protect contents from light, air, and moisture, which helps preserve the quality of items such as fish oil, capsules, and vitamins.
- Add verified safety features. Tamper-evident and child-resistant closures support compliance and product integrity standards.
- Use eco-friendly options. Recyclable cartons, biodegradable fillers, and Forest Stewardship Council (FSC)-certified paper are increasingly used to align with sustainability initiatives and consumer expectations.
- Follow labeling requirements. Each label must include accurate ingredient listings, a Supplement Facts panel, mandatory label elements, and truthful, non-misleading statements. For structure/function claims, the mandatory FDA disclaimer (“This statement has not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. This product is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.”) must be clearly displayed. Batch or lot numbers and clear expiration dates also aid traceability.
Properly chosen packaging materials and accurate labeling protect supplement quality throughout the supply chain and enhance customer satisfaction without suggesting any medical or therapeutic benefits.
What Compliance Rules Apply to Supplement Packaging
Compliance for nutraceutical packaging centers on documentation, facility control, and labeling accuracy under 21 CFR Part 111. While packaging compliance focuses on process and recordkeeping, the FDA separately regulates product claims, requiring disclaimers for structure/function statements and prohibiting disease claims.
- Follow FDA 21 CFR Part 111. These Current Good Manufacturing Practice regulations define packaging and storage requirements for dietary supplements.
- Understand FDA oversight. The FDA does not “approve” supplements before sale but may inspect facilities for recordkeeping, sanitation, and labeling compliance.
- Validate all equipment. Contract packaging systems must be clean, maintained, and properly documented to prevent mix-ups or contamination.
- Ensure traceability. Each container requires batch and lot information, plus expiration dates for potential recalls.
- Meet retailer standards. Some distributors or stores may require National Sanitation Foundation (NSF) Certified for Sport or NSF Contents Certified verification before listing products.
Following these compliance steps establishes traceable, verifiable standards within supplement packaging and logistics, protecting both consumers and companies without implying medical performance.

How to Manage Storage and Fulfillment Efficiently
Storage and fulfillment services preserve supplement quality between manufacturing and final delivery. Controlled environments and precise inventory systems help maintain labeling accuracy and timely distribution.
How Climate Control and Shelf Life Affect Storage
Temperature and humidity have measurable effects on dietary supplements, which must be stored in stable, sanitary conditions to remain within labeled specifications.
- Maintain controlled environments. Warehouses should stay dry, ventilated, and within recommended temperature limits to prevent product degradation of powders, tablets, or softgels.
- Apply rotation systems. Use FIFO (First In, First Out) or FEFO (First Expiring, First Out) practices to manage stock efficiently.
- Track and record conditions. Use temperature-monitoring devices to log environmental data for storage and shipping.
- Protect sensitive forms. Probiotics, softgels, and liquids often require humidity control to maintain label-stated stability.
- Work with compliant facilities. GMP-compliant fulfillment centers are designed for supplement handling, with required hygiene documentation and inspection readiness.
Even brief exposure to extreme conditions may affect product stability or consistency. Continuous monitoring ensures logistics compliance and consistent product quality.
How to Coordinate Shipping to Amazon or 3PL Centers
Shipping supplement products involves strict coordination with retailers and third-party logistics (3PL) centers that follow labeling and documentation standards.
- Choose experienced logistics providers. Work with a logistics company familiar with supplement fulfillment services to maintain accuracy in labeling, packing, and recordkeeping.
- Follow retailer routing rules. Amazon Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) and other platforms enforce standardized labeling, carton specifications, and expiration date tracking.
- Use validated technology. Temperature sensors and insulated packaging materials help preserve quality during transport.
- Maintain documentation. Keep packing slips, chain-of-custody records, and shipment logs for audit readiness.
- Locate warehouses strategically. Regional hubs shorten delivery times, lower shipping costs, and improve reliability for supplements online.
Consistent, fast shipping supports repeat business for brands offering vitamins, protein powders, or pet supplements, without making any claims about product effects or benefits.

How to Handle Scaling and Expedited Orders
As production expands, strong packaging solutions and scalable logistics systems help companies manage growth efficiently and remain compliant.
When to Prepare for Seasonal or Sudden Demand Spikes
Anticipating increased demand keeps the supply chain organized and prevents shortages.
- Use sales forecasts. Analyze order patterns and lead times to predict seasonal surges.
- Create safety stock. Maintain additional packaging materials and ingredients for busy months, such as year-end wellness promotions.
- Adopt flexible equipment. Modular bottling or pouching lines can scale quickly while maintaining documentation accuracy.
- Plan for urgent shipping. Have contingency carriers ready for unexpected marketing-driven demand.
Planning 60–90 days ahead helps maintain customer satisfaction and operational compliance during rapid sales cycles.
How to Communicate Delivery Timelines with Your Manufacturer
Reliable communication keeps supply fulfillment and production schedules aligned.
- Schedule regular updates. Maintain open contact among brand owners, contract manufacturers, and warehouse teams.
- Set defined Service Level Agreements (SLAs). Establish timelines for packaging completion, Quality Assurance (QA) release, and shipping readiness.
- Track performance. Shared dashboards improve visibility and prevent costly delays.
- Document everything. Clear written communication supports GMP and FDA expectations for recordkeeping.
Proactive coordination reduces shipping errors and ensures every supplement product reaches consumers on time without implying any medical or performance outcomes.

Founder’s Checklist for Packaging and Logistics Readiness
Before launch, founders should confirm that packaging and fulfillment meet compliance and operational standards.
☐ Packaging verified for FDA and GMP specifications
☐ Climate-control systems tested and logged
☐ 3PL documentation reviewed for accuracy
☐ Batch tracking and recall procedures validated
☐ Tamper-evident and eco-friendly options implemented
Effective supplement packaging and logistics ensure consistent product quality and regulatory adherence across every shipment.
Building Long-Term Success Through Smarter Supplement Packaging and Logistics
From production lines to delivery routes, operational control defines the reliability of every supplement brand. Success depends on five core pillars: packaging integrity, labeling accuracy, temperature-controlled storage, fulfillment precision, and transparent communication. Together, these elements ensure FDA and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance while protecting both the product and the brand.
Maintaining accurate records, temperature logs, and inspection reports helps prevent issues like expired or heat-damaged inventory. Companies that invest in disciplined supplement packaging and logistics create custom solutions that meet their clients’ specific needs while improving efficiency and minimizing waste.
When every shipment is properly labeled, protected, and delivered on time, it represents a complete system built for consistency and trust. These optimized packaging options help brands save money, retain loyal clients, and strengthen their reputation across the market. Businesses that commit to continuous improvement in packaging and logistics discover how operational excellence translates directly into long-term success throughout the supply chain.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the FDA packaging requirements for supplements?
Dietary supplements must meet FDA 21 CFR Part 111 standards for labeling accuracy, sanitation, and recordkeeping; the FDA does not pre-approve products before sale.
How long do supplements last in storage?
Shelf life depends on formulation and storage conditions, but products generally remain stable within their labeled expiration period when kept cool and dry.
Can I ship supplements directly from the manufacturer?
Yes, provided that the contract packaging and fulfillment services follow all GMP and FDA storage and labeling requirements.
How do I prepare for peak-season demand?
Plan production early, maintain extra packaging materials, and coordinate with suppliers at least two months before expected surges.
What are the most common packaging errors?
Typical issues include incorrect labels, missing expiration dates, poor seals, or the use of improper packaging materials for moisture-sensitive items.
References
- Code of Federal Regulations. (2025, September 29). Title 21, Part 111—Current good manufacturing practice in manufacturing, packaging, labeling, or holding operations for dietary supplements. Electronic Code of Federal Regulations. https://www.ecfr.gov/current/title-21/chapter-I/subchapter-B/part-111
- Fenster, K., Freeburg, B., Hollard, C., Wong, C., Rønhave Laursen, R., & Ouwehand, A. C. (2019). The production and delivery of probiotics: A review of a practical approach. Microorganisms, 7(3), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms7030083
- Food and Drug Administration. (2005, April). Dietary supplement labeling guide. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements-guidance-documents-regulatory-information/dietary-supplement-labeling-guide
- Food and Drug Administration. (2022, June 2). FDA 101: Dietary supplements. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/fda-101-dietary-supplements
- Food and Drug Administration. (2024, April 24). Current good manufacturing practices (CGMPs) for food and dietary supplements. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.fda.gov/food/guidance-regulation-food-and-dietary-supplements/current-good-manufacturing-practices-cgmps-food-and-dietary-supplements
- NSF International. (2024, February 8). What is NSF certification? https://www.nsf.org/knowledge-library/what-is-nsf-certification